What Is Netbios Used For
NetBIOS: what it is, how it works and how to employ in information security
Table of contents
i. What is NetBIOS?
2. NetBIOS Services
ii.1 Name service (NetBIOS-NS)
2.2 Datagram distribution service (NetBIOS-DGM)
2.iii Session service (NetBIOS-SSN)
three. NetBIOS proper noun vs Internet host name
three.1 NetBIOS name
3.2 Cyberspace host name
4. How to detect NetBIOS
five. nbtstat
6. Wireshark filters for highlighting NetBIOS traffic
7. LMHOSTS file
8. NetBIOS exploitation
viii.ane Invoke-Inveigh
8.2 Responder
viii.3 NMBscan
8.4 NetBIOS Share Scanner
viii.5 NBTscan
8.half-dozen nbtscan-unixwiz
8.7 fakenetbios
eight.8 nbnspoof
viii.ix nbtenum
eight.10 nbtool
8.11 nbname
8.12 Online scanners on SuIP.biz
Every Windows computer has a computer name. Even if y'all did not set information technology, thenthe name generated during the installation of the operating arrangement is written there.
This computer name on the local network can exist used as a complete culling to the local IP address:
- admission shares (network folders and printers)
- access running network services (web server, FTP, etc.)
See the article "Windows Calculator proper name: how to alter and employ" for more details.
Information technology does non require any configuration of the DNS or hosts file, since such name recognition is provided by NetBIOS. We have already encountered NetBIOS, or rather, one of its three services – NBT-NS – in the article "Windows Network Authentication Hacking". This is 1 of the services that was used to perform the set on.
That is, NetBIOS is important for Windows, as well as for earthworks in the Windows architecture, analyzing the network activity of Windows and the security bug of local networks and Windows computers.
Naturally, in the all-time traditions of Miloserdov.org, the article will contain just the necessary theory and maximum practise – nosotros volition 'probe' the NetBIOS protocol in Wireshark, the born Windows utility and in specialized tools for security auditing. Merely let'southward start with the theory.
What is NetBIOS?
NetBIOS is an acronym for Network Basic Input/Output Organization. Information technology provides services related to the session layer of the OSI model assuasive applications on carve up computers to communicate over a local area network. As strictly an API, NetBIOS is not a networking protocol. Older operating systems[clarification needed] ran NetBIOS over IEEE 802.2 and IPX/SPX using the NetBIOS Frames (NBF) and NetBIOS over IPX/SPX (NBX) protocols, respectively. In modern networks, NetBIOS ordinarily runs over TCP/IP via the NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NBT) protocol. This results in each computer in the network having both an IP address and a NetBIOS proper name corresponding to a (possibly different) host proper noun.
Applications can find through NETBIOS the resources they demand, establish a connection and transport or receive information. NETBIOS uses port 137 for the name service, port 138 for the datagram service, and port 139. For sessions, any session starts with a NETBIOS request, specifying the IP address and determining the TCP port of the remote object, followed past the exchange of NETBIOS messages, later on bringing the session to a close. The session exchanges information between two NETBIOS applications. The message length ranges from 0 to 131071 bytes. The simultaneous institution of several sessions between two objects is acceptable. When organizing IP send via NETBIOS, the IP datagram is embedded in the NETBIOS bundle. Data exchange occurs in this case without establishing a connection between the objects. NETBIOS names must contain IP addresses. Then, part of the NETBIOS accost can be of the form IP .**.**.**.**, where IP indicates the blazon of functioning (IP via Netbios), and **.**.**.** is an IP- address. NETBIOS system has its ain organization of commands (call, listen, hang up, send, receive, session status, reset, cancel, adapter condition, unlink, remote program load) and primitives for working with datagrams (ship datagram, send broadcast datagram, receive datagram , receive broadcast datagram). All NETBIOS end nodes are divided into three types:
- circulate ("b") nodes
- bespeak-to-signal nodes ("p");
- nodes of the mixed type ("m").
An IP accost can be associated with 1 of these types. B-nodes communicate with their partner through circulate requests. P and M nodes apply netbios proper noun server (NBNS) and datagram distribution server (NBDD) for this purpose.
NetBIOS Services
NetBIOS provides three distinct services:
- Name service (NetBIOS-NS) for name registration and resolution.
- Datagram distribution service (NetBIOS-DGM) for connectionless communication.
- Session service (NetBIOS-SSN) for connection-oriented communication.
(Note: SMB, an upper layer, is a service that runs on pinnacle of the Session Service and the Datagram service, and is not to be confused as a necessary and integral part of NetBIOS itself. It can now run atop TCP with a modest adaptation layer that adds a parcel length to each SMB bulletin; this is necessary considering TCP only provides a byte-stream service with no notion of packet boundaries.)
Proper noun service (NetBIOS-NS)
In gild to start sessions or distribute datagrams, an application must register its NetBIOS proper noun using the proper name service. NetBIOS names are 16 octets in length and vary based on the particular implementation. Oft, the 16th octet, called the NetBIOS Suffix, designates the blazon of resource, and can be used to tell other applications what blazon of services the system offers. In NBT, the name service operates on UDP port 137 (TCP port 137 tin besides be used, but rarely is).
The name service primitives offered past NetBIOS are:
- Add name – registers a NetBIOS proper noun.
- Add grouping name – registers a NetBIOS "group" proper name.
- Delete name – united nations-registers a NetBIOS name or group proper name.
- Find name – looks upwardly a NetBIOS name on the network.
NetBIOS proper noun resolution is not supported by Microsoft for Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6).
Datagram distribution service (NetBIOS-DGM)
Datagram mode is connectionless; the application is responsible for fault detection and recovery. In NBT, the datagram service runs on UDP port 138.
The datagram service primitives offered by NetBIOS are:
- Send Datagram – send a datagram to a remote NetBIOS name.
- Send Broadcast Datagram – transport a datagram to all NetBIOS names on the network.
- Receive Datagram – wait for a packet to arrive from a Send Datagram performance.
- Receive Broadcast Datagram – wait for a bundle to arrive from a Send Circulate Datagram performance.
Session service (NetBIOS-SSN)
Session mode lets two computers establish a connection, allows messages to span multiple packets, and provides error detection and recovery. In NBT, the session service runs on TCP port 139.
The session service primitives offered past NetBIOS are:
- Telephone call – opens a session to a remote NetBIOS proper noun.
- Listen – heed for attempts to open a session to a NetBIOS name.
- Hang Up – close a session.
- Send – sends a package to the computer on the other terminate of a session.
- Send No Ack – like Send, merely doesn't require an acquittance.
- Receive – look for a packet to arrive from a Send on the other end of a session.
In the original protocol used to implement NetworkBIOS services on PC-Network, to establish a session, the initiating computer sends an Open request which is answered by an Open acknowledgment. The computer that started the session will then transport a Session Request packet which will prompt either a Session Accept or Session Reject bundle.
During an established session, each transmitted package is answered by either a positive-acknowledgment (ACK) or negative-acknowledgment (NAK) response. A NAK will prompt retransmission of the data. Sessions are closed past the non-initiating calculator by sending a close request. The computer that started the session will reply with a close response which prompts the final session airtight packet.
NetBIOS name vs Internet host name
When NetBIOS is run in conjunction with Internet protocols (eastward.yard., NBT), each computer may have multiple names: one or more NetBIOS name service names and 1 or more than Internet host names.
NetBIOS proper name
The NetBIOS proper name is sixteen ASCII characters, all the same Microsoft limits the host name to 15 characters and reserves the 16th character equally a NetBIOS Suffix. This suffix describes the service or name record type such as host record, master browser tape, or domain controller record or other services. The host proper noun (or short host name) is specified when Windows networking is installed/configured, the suffixes registered are determined by the private services supplied by the host. In club to connect to a computer running TCP/IP via its NetBIOS proper noun, the proper name must be resolved to a network address. Today this is usually an IP address (the NetBIOS name to IP address resolution is frequently done by either broadcasts or a WINS Server – NetBIOS Name Server). A computer's NetBIOS proper noun is frequently the same every bit that computer's host name (see below), although truncated to xv characters, but information technology may besides exist completely different.
NetBIOS names are a sequence of alphanumeric characters. The post-obit characters are explicitly not permitted: \/:*?"<>|. Since Windows 2000, NetBIOS names also had to comply with restrictions on DNS names: they cannot consist entirely of digits, and the hyphen ("-") or full-stop (".") characters may not announced as the first or last character. Since Windows 2000, Microsoft has advised confronting including any full-stop (".") characters in NetBIOS names, such that applications tin utilise the presence of a full-stop to distinguish domain names from NetBIOS names.
The Windows LMHOSTS file provides a NetBIOS name resolution method that can be used for modest networks that do not use a WINS server.
Net host proper noun
A Windows machine's NetBIOS proper name is non to be confused with the figurer's Cyberspace host name (assuming that the computer is also an Net host in addition to being a NetBIOS node, which need not necessarily be the example). Mostly a computer running Internet protocols (whether it is a Windows machine or not) usually has a host name (besides sometimes called a auto proper noun). Originally these names were stored in and provided by a hosts file but today almost such names are part of the hierarchical Domain Name System (DNS).
Generally the host proper name of a Windows reckoner is based on the NetBIOS proper name plus the Primary DNS Suffix, which are both set up in the System Properties dialog box. At that place may also exist connection-specific suffixes which tin can be viewed or changed on the DNS tab in Command Panel → Network → TCP/IP → Avant-garde Properties. Host names are used by applications such as telnet, ftp, web browsers, etc. To connect to a calculator running the TCP/IP protocol using its proper noun, the host name must be resolved into an IP accost, typically by a DNS server. (It is likewise possible to operate many TCP/IP-based applications, including the three listed above, using just IP addresses, but this is not the norm.)
How to detect NetBIOS
You tin run a regular scan of TCP ports on a LAN using nmap:
sudo nmap _gateway/24
And amidst the results yous can discover open TCP port 139:
139/tcp open netbios-ssn

If nosotros are just interested in NetBIOS services, then it'southward enough to look for UDP ports 137 and 138 and TCP ports 137 and 139, use Nmap usage tips and compose this control:
sudo nmap -p U:137,138,T:137,139 -sU -sS _gateway/24
The advantage of this approach is that scanning is much faster and additional open UDP ports are institute.

You can use another Nmap usage tip to collect service banners, for this we add the -sV --script=banner options:
sudo nmap -p U:137,138,T:137,139 -sU -sS -sV --script=banner _gateway/24
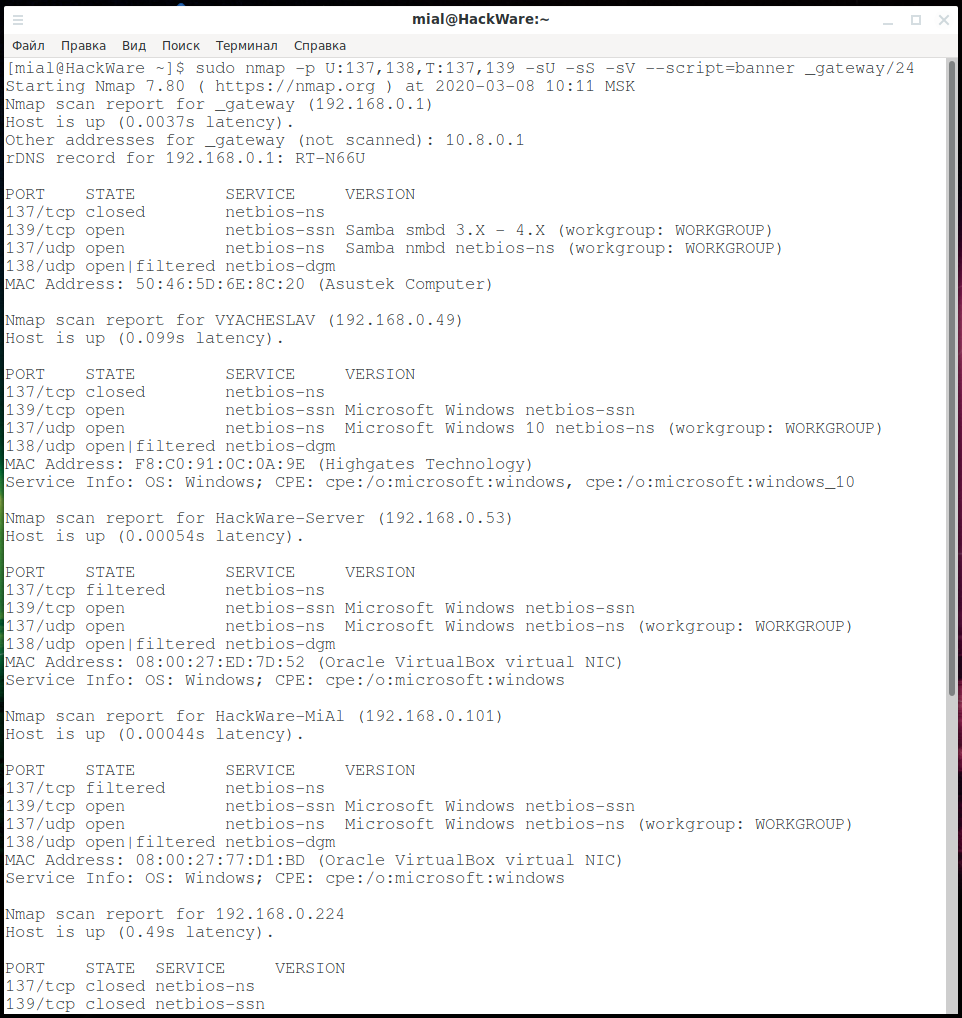
Thanks to the last command, we additionally discovered:
- used workgroup (WORKGROUP)
- operating arrangement for some devices (Windows 10)
- some open ports are associated with Samba smbd three.X - 4.10
Additionally, you can utilize Nmap scripts (NSE) – I institute four scripts that are related to NetBIOS:
nbd-info
Displays protocol and block device data from NBD servers.
nbstat
Attempts to recall the target's NetBIOS names and MAC address.
broadcast-netbios-master-browser
Attempts to discover primary browsers and the domains they manage.
nbns-interfaces
Retrieves IP addresses of the target'south network interfaces via NetBIOS NS. Additional network interfaces may reveal more information nearly the target, including finding paths to subconscious non-routed networks via multihomed systems.
To use them during a scan, the command is approximately the following:
sudo nmap -p U:137,138,T:137,139 -sU -sS --script nbstat,nbd-info,circulate-netbios-chief-browser,nbns-interfaces _gateway/24
Results:

nbtstat
The nbtstat programme is designed to display NetBIOS protocol statistics and current TCP/IP connections using NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP). The nbtstat program is preinstalled on Windows, that is, it does not demand to be downloaded and installed, but information technology must be run on the control line. Encounter "How to gear up the PowerShell environs on Windows and Linux".
Usage:
NBTSTAT [ [-a RemoteName] [-A IP address] [-c] [-due north] [-r] [-R] [-RR] [-southward] [-Southward] [interval] ]
Options:
-a (adapter status) Lists the remote auto's name table given its name -A (Adapter condition) Lists the remote motorcar'southward proper name table given its IP accost. -c (enshroud) Lists NBT's cache of remote [machine] names and their IP addresses -north (names) Lists local NetBIOS names. -r (resolved) Lists names resolved past broadcast and via WINS -R (Reload) Purges and reloads the remote cache name tabular array -S (Sessions) Lists sessions table with the destination IP addresses -southward (sessions) Lists sessions tabular array converting destination IP addresses to figurer NETBIOS names. -RR (ReleaseRefresh) Sends Proper name Release packets to WINS and and then, starts Refresh RemoteName Remote host machine proper noun. IP address Dotted decimal representation of the IP address. interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds betwixt each display. Press Ctrl+C to end redisplaying statistics.
Permit'south consider examples of using nbtstat.
To find out the host proper name by IP address, use the -A option:
nbtstat -A 192.168.0.53

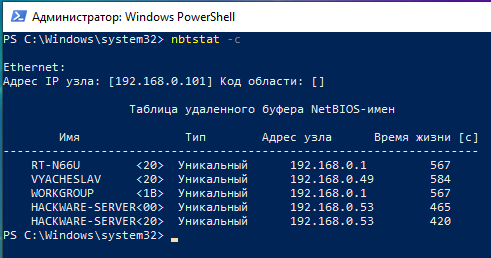
To view the names of computers and their IPs stored in the cache use the -c option:
nbtstat -c
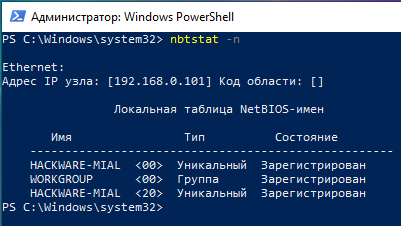
To find out the name of the current computer use nbtstat with the-n selection:
nbtstat -n
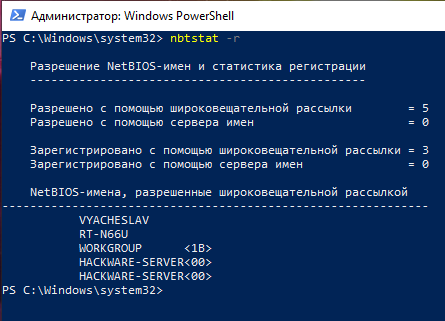
To listing names resolved by broadcast and via WINS run the control:
nbtstat -r
Wireshark filters for highlighting NetBIOS traffic
Wireshark supports almost all network protocols (see "Wireshark Filters"), including NetBIOS protocols.
Wireshark Filter for Proper noun Service (NetBIOS-NS):
nbns
A broadcast request to determine the IP address past estimator name:
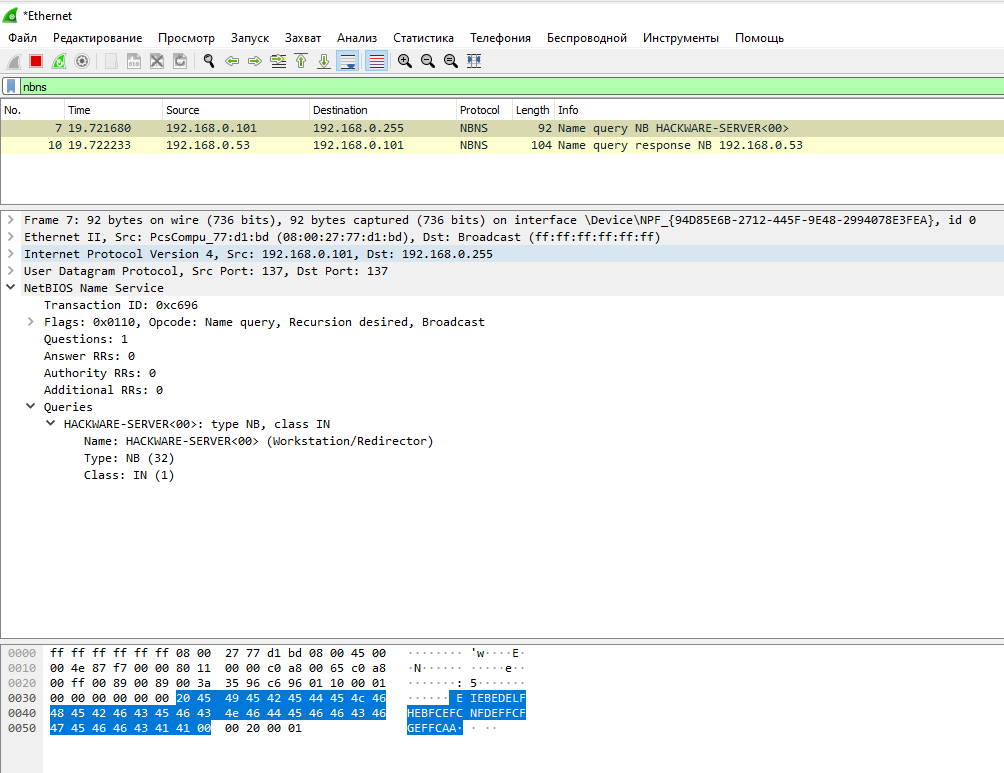
Received response:
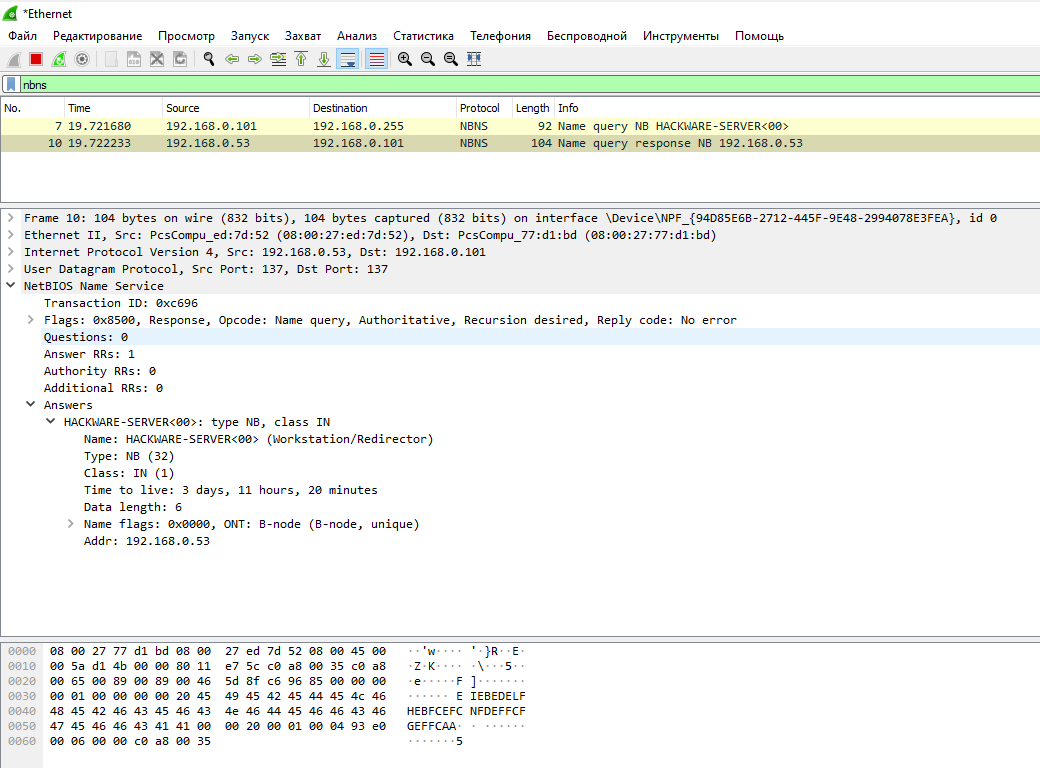
A request to a specific host to obtain its host proper noun:

Received response:

Wireshark Filter for Datagram Distribution Service (NetBIOS-DGM):
nbdgm

Wireshark Filter for Session Service (NetBIOS-SSN):
nbss
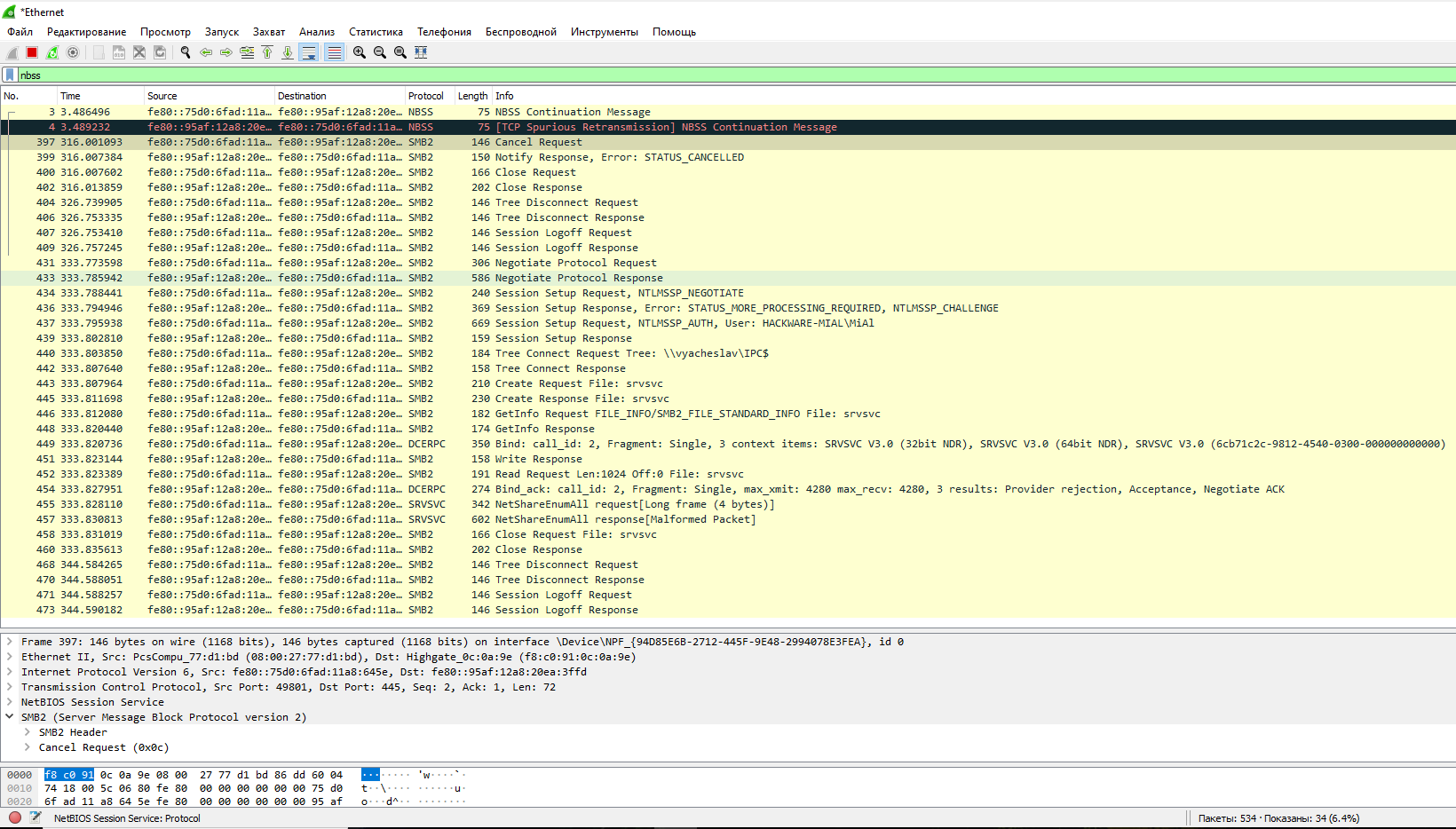
To filter all NetBIOS traffic:
nbns or nbdgm or nbss
LMHOSTS file
The LMHOSTS (LAN Manager Hosts) file is used to enable Domain Name Resolution under Windows when other methods, such equally WINS, fail. It is used in conjunction with workgroups and domains. If you are looking for a elementary, general mechanism for the local specification of IP addresses for specific hostnames (server names), utilize the HOSTS file, not the LMHOSTS file.
The file, if information technology exists, is read as the LMHOSTS setting file. A sample file (lmhosts.sam) is provided. It contains documentation for manually configuring the file.
File Locations: in Windows NT four.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Vista, seven, 8, 10, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016+ the file is located in %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\, and a sample file (lmhosts.sam) is installed here. Notation that %windir% is an environment variable pointing to the Windows installation directory, normally C:\Windows.
The syntax for the LMHOSTS file is the same as for HOSTS, i.east.:
IP_ADDRESS HOST_NAME
NetBIOS exploitation
NetBIOS security audit program can be divided into 2 groups:
- NetBIOS spoofing to perform homo-in-the-middle attacks
- NetBIOS scan to collect information
The programs for scanning NetBIOS are mostly abandoned, since virtually all information (name, IP, MAC address) tin be gathered either by the standard Windows utility or by the Nmap scanner.
As for NetBIOS spoofing tools, there are quite a few mordern programs amidst them, usually including spoofing of NetBIOS services equally part of a complex attack.
The following is a cursory overview of the tools, since the scanning tools are too simple to talk virtually them much, and the spoofing tools are too complex to exist considered in this commodity – each of them deserves its own commodity or even a few tutorials on their various functions.
Invoke-inveigh
Inveigh is a PowerShell ADIDNS/LLMNR/NBNS/mDNS/DNS spoofer and a homo-in-the-middle attack tool designed to help penetration testers/red timers that are limited to Windows.
Inveigh tutorials are being prepared for this program for Miloserdov.org website.
An example of starting an inspectation without attack:
Import-Module ./Inveigh.psd1 Invoke-Inveigh -Audit -ConsoleOutput Y
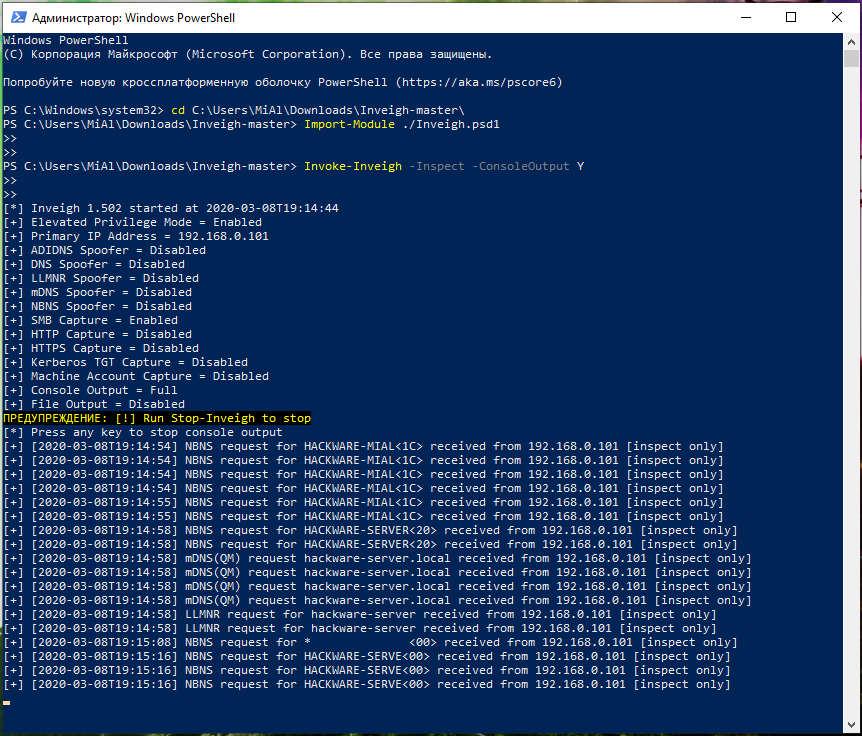
Response
Responder is a tool for performing a man-in-the-centre assault against hallmark methods in Windows. This programme includes the LLMNR, NBT-NS and MDNS poisoner, thanks to which traffic is redirected with requests and authentication hashes. The program also includes HTTP/SMB/MSSQL/FTP/LDAP authentication rogue servers that back up authentication methods such as NTLMv1/NTLMv2/LMv2, Extended Security NTLMSSP and basic HTTP authentication, for which the Responder acts as a relay.
Detailed instructions for using the Responder 'Windows Network Authentication Hacking'.
NMBscan
NMBscan scans the shares of a SMB/NetBIOS network, using the NMB/SMB/NetBIOS protocols. It is useful for acquiring data on a local area network for such purposes as security auditing.
It can obtain such information as NMB/SMB/NetBIOS/Windows hostname, IP address, IP hostname, ethernet MAC address, Windows username, NMB/SMB/NetBIOS/Windows domain proper noun, and master browser.
Information technology tin can detect all the NMB/SMB/NetBIOS/Windows hosts on a local area network past using the hosts lists maintained by chief browsers.
Installation manual: https://en.kali.tools/?p=1736
Launch Instance:
nmbscan -h 192.168.0.101 -h 192.168.0.1 -h 192.168.0.53
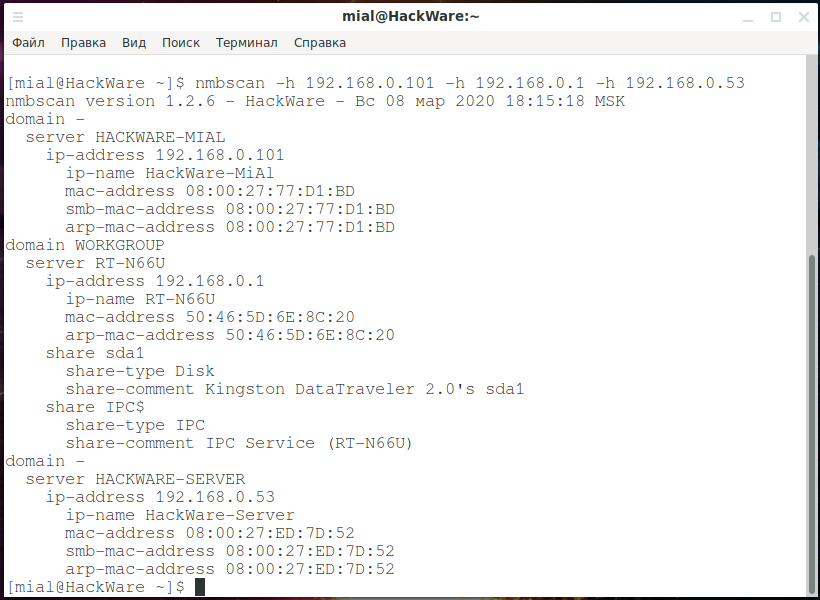
To browse a subnet (very dull):
nmbscan -h 192.168.0.{ane..255} NetBIOS Share Scanner
NetBIOS Share Scanner can exist used to bank check Windows workstations and servers if they have available shared resources.
Launch Example:
netbios-share-scanner 192.168.0.ane
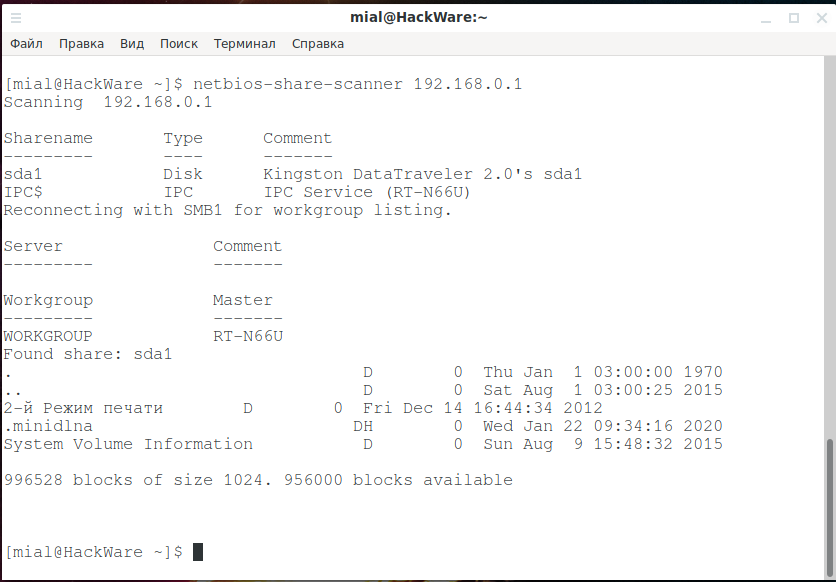
Installation manual, as well as boosted examples of utilize: https://en.kali.tools/?p=1729
NBTscan
NBTscan is an IP scanning program for retrieving NetBIOS proper name information.
Scans the whole 192.168.1.0/24 network:
nbtscan -r 192.168.1.0/24

Installation manual, besides as additional examples of use: https://en.kali.tools/?p=1723

nbtscan-unixwiz
nbtscan-unixwiz is a command line tool that scans for open NETBIOS name servers on a local or remote TCP/IP network, the starting time step in finding open shares. It is based on the functionality of the standard Windows nbtstat tool, but it can work not but with a unmarried address, but also with a range of addresses.
The tool has a version for Windows and Linux.
Scan a range of IP addresses (192.168.0.100-110) without performing contrary name resolutions (-n):
nbtscan-unixwiz -n 192.168.0.100-110
Scan the specified IP addresses (192.168.1.36 192.168.1.threescore 192.168.1.61 192.168.1.63), display all received data (-f), make 3 attempts per IP address (-t 3):
nbtscan-unixwiz -f -t three 192.168.1.36 192.168.i.60 192.168.ane.61 192.168.ane.63

Installation manual, besides as additional examples of use: https://en.kali.tools/?p=1744
fakenetbios
A family of tools designed to simulate Windows hosts (NetBIOS) on a LAN (local surface area network).
Link: https://github.com/mubix/FakeNetBIOS
nbnspoof
NetBIOS Services Name Spoofer.
The source code of the program (written in Python2).
nbtenum
A utility for Windows that tin be used to list NetBIOS information from a single host or range of hosts. To run on Windows.
Source code: http://dl.packetstormsecurity.net/Win/NBTEnum33.cypher
nbtool
Several tools for exploring, attacking and communicating with NetBIOS and DNS.
Link: https://wiki.skullsecurity.org/Nbtool
nbname
Decodes and displays all the names of NetBIOS packets received on UDP port 137 and more! To run on Windows.
Link: ftp://ftp.mrynet.com/operatingsystems/DEC/vmsone/vmsone.com/~decuslib/vmssig/vmslt01b/net/nbname.exe
The last program did not work for me.
Online scanners on SuIP.biz
The NetBIOS, SMB (NetBIOS) and Samba (Linux) online scanner uses a number of the tools described higher up to collect primary information on NetBIOS and SMB (Samba). It is enough to specify the IP address of the target and several tools will starting time scanning at once, which volition bear witness the version of running services, the computer name and workgroup (domain), try to perform an bearding login and show shared folders if they are available.



What Is Netbios Used For,
Source: https://miloserdov.org/?p=4261
Posted by: deloachexamseaten.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Netbios Used For"
Post a Comment